ExOR - Extremely Opportunistic Routing: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{| style="float:left; background:transparent; padding:0px; margin:0px;" |
{| style="float:left; background:transparent; padding:0px; margin:0px;" |
||
|- valign="top" |
|- valign="top" |
||
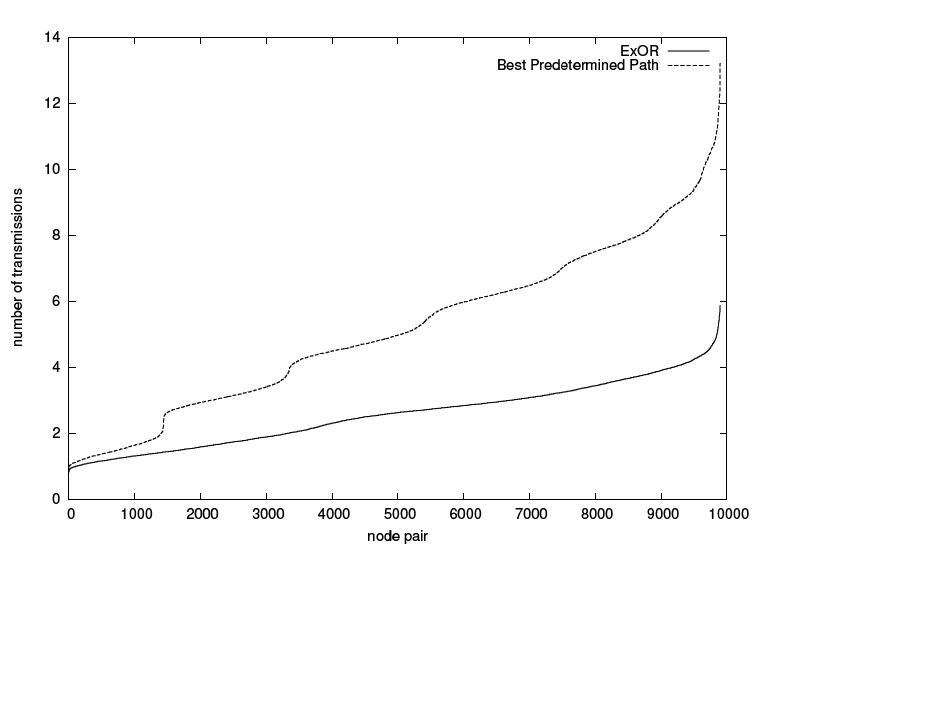
|[Image:transmissions.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Number of Transmissions per node pair] |
|[[Image:transmissions.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Number of Transmissions per node pair]] |
||
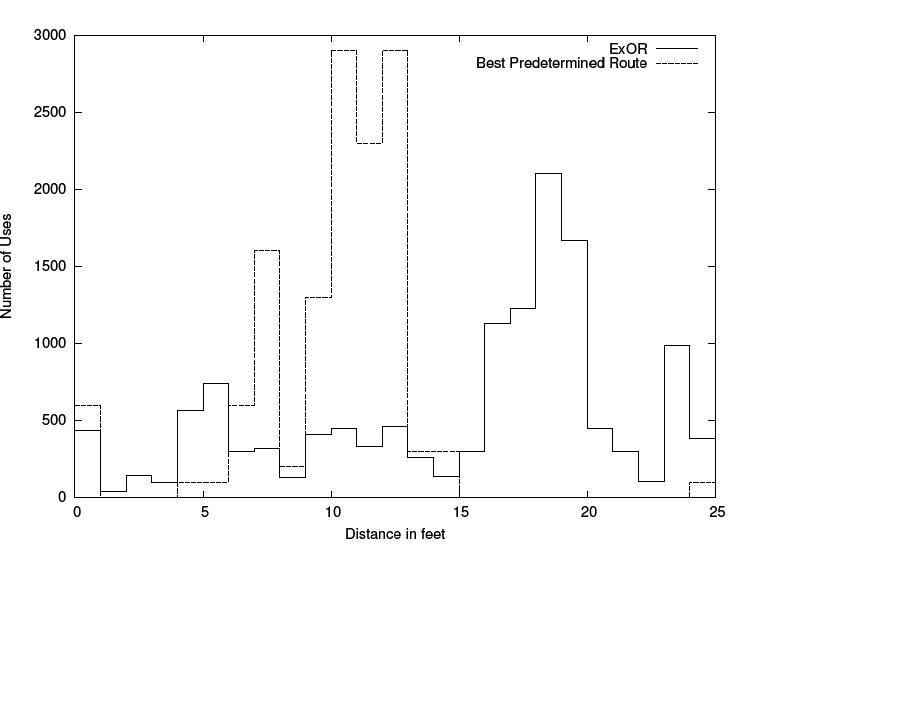
|[Image:distribution.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Number of used nodes in correlation with distance] |
|[[Image:distribution.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Number of used nodes in correlation with distance]] |
||
|{subst:Absatz-L}} |
|{subst:Absatz-L}} |
||
Revision as of 11:35, 23 July 2007
Description
Extremely Opportunistic Routing is a Routing algorithm that takes advantage of the characteristics of wireless networks. Therefor ExOR determines the path as the packet moves through the network instead of choosing a single route ahead of time.
Implementation
Performance
In comparison to many well-known Routing - algorithms like OSPF,DSR,AODV Opportunistic routing generally performs better than the a margin of 55%. Depending on how large the network is there are improvements of up to 65%. In generell the the greatest benefit out of ExOR is its ability to skip intermediate hops.
| {subst:Absatz-L}}
The first graphic shows how ExOR reduces the number of Transmissions in a network. ProblemsSee alsoExternal Links |