ExOR - Extremely Opportunistic Routing
Description
Extremely Opportunistic Routing is a Routing algorithm that takes advantage of the characteristics of wireless networks. Therefor ExOR determines the path as the packet moves through the network instead of choosing a single route ahead of time. Through this improvement the performance in wireless networks will increase significantly.
Implementation
What is neccesary to implement such a routing protocol?
First the standard MAC Protocol has to be modified. And in second every node needs a Delivery-Ratio-Matrix to decide which node would be the best receiver.
Modified MAC Protocol
The standard MAC Protocol is used to define the format for data transmission. Therefor its frame has several partitions.
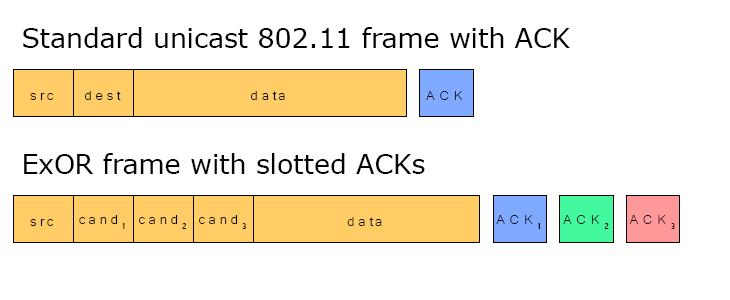 |
The ExOR algorithm needs to improve the current MAC - Protocol as it changes the single destination and acknowledgement partition into a n-slot partition. E.G. the network where ExOR will be implemented needs a 3 candidate list, there will be 3 destination slots and 3 acknowledgement slots like it is shown in the picture.
Delivery - Ratio MAtrix
The Delivery - Ratio Matrix consists of transmission rates between each node in the network. Consequently every node owns such a matrix. All Values are updated in a specific period of time through a link-state-flooding scheme. Though it is possible to keep up with changes within the network
Performance
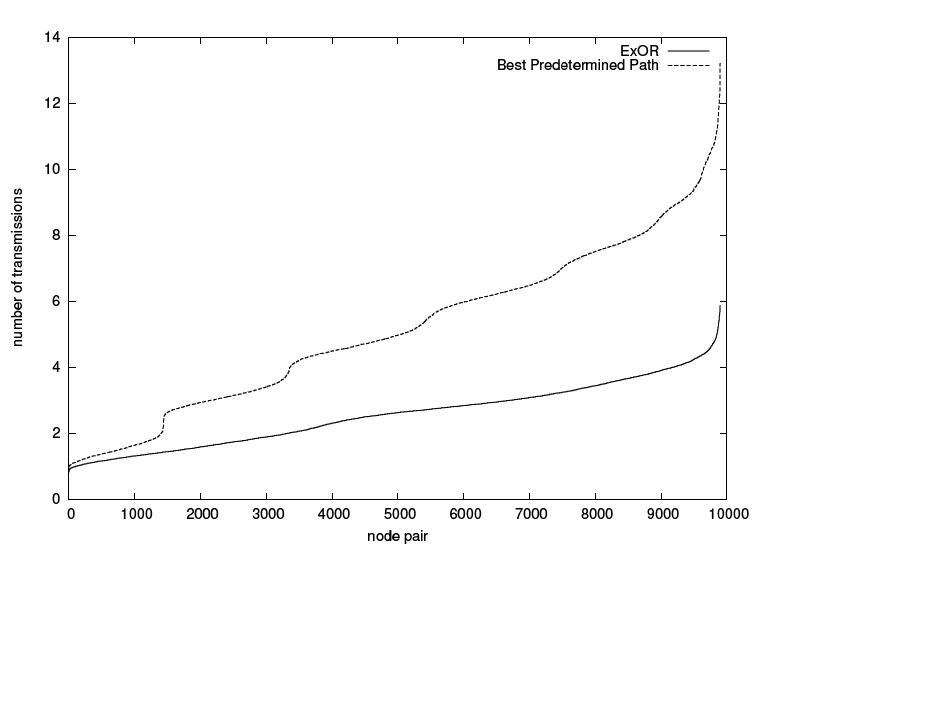
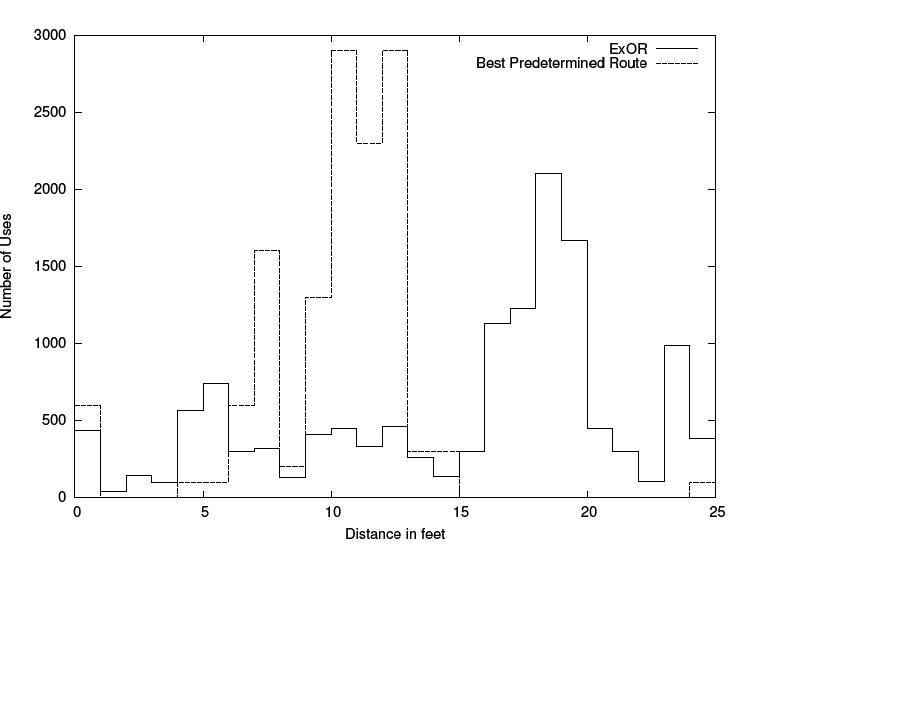
In comparison to many well-known Routing - algorithms like OSPF,DSR,AODV Opportunistic routing generally performs better than the a margin of 55%. Depending on how large the network is there are improvements of up to 65%. In generell the greatest benefit out of ExOR is its ability to skip intermediate hops.
 |
 |
The first graphic shows how ExOR reduces the number of Transmissions in a network.