Yubikey: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Yubikey == |
== Yubikey == |
||
* USB-Token |
* USB-Token |
||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
== Yubikey == |
== Yubikey == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
=== OTP === |
=== OTP === |
||
* ''secret'': 128-bit AES key |
* ''secret'': 128-bit AES key |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
* Validierung der OTPs übernimmt ein Validation Server der via HTTP ansprechbar ist |
* Validierung der OTPs übernimmt ein Validation Server der via HTTP ansprechbar ist |
||
* http://code.google.com/p/yubikey-val-server-php/wiki/ValidationProtocolV20 |
* http://code.google.com/p/yubikey-val-server-php/wiki/ValidationProtocolV20 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Validation === |
=== Validation === |
||
Latest revision as of 15:12, 27 April 2012
Yubikey
- USB-Token
- One-Time Password Generator
Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung
- Besitz und Wissen
- z.B.
- nPA eID(PIN + Ausweis)
- Online-Banking
- iTAN (Passwort + TAN-Liste)
- ChipTAN (Passwort + EC-Karte)
- smsTAN (Passwort + SIM-Karte)
Yubikey: OTP als Nachweis für den Besitz eines bestimmten Tokens.
One-Time Passwords
- generell
- moving factor MF: z.B. counter, timestamp
- secret S
- otp = f(S, MF)
- konkret
- Yubikey OTP
- OATH - Initiative for open authentication
- HOTP HMAC-Based One-time Password Algorithm (RFC 4226)
- TOTP Time-based One-time Password Algorithm (RFC 6238)
- OCRA OATH Challenge Response Algorithm (RFC 6287)
Yubikey
OTP
- secret: 128-bit AES key
- moving factor: (3) Counter
- session counter (16 bit)
- session use counter (8 bit)
- timestamp (24 bit)
- public id (48 bit)
- private id (48 bit)
internal id s.count timestamp s.use random crc
ccff5e92d4e8 0003 275ab5 01 ead3 e90e
\ \ | / / /
ccff5e92d4e80300b55a2701d3ea0ee9
|
aes_encrypt(S)
public id |
ffda638233c7 1cd02dd852d50fbb5acb4c6808062625
\ |
ffda638233c71cd02dd852d50fbb5acb4c6808062625
|
modhex_encode()
|
vvtlhejdeeribrtcdttjgdtgcvnnglrnfrhjcjchdhdg
Validation Protocol
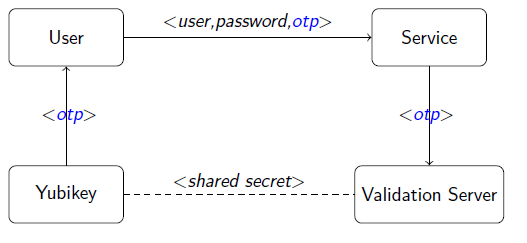
- Validierung der OTPs übernimmt ein Validation Server der via HTTP ansprechbar ist
- http://code.google.com/p/yubikey-val-server-php/wiki/ValidationProtocolV20
Validation
- Entschlüsselung des OTP mit shared secret
- CRC-Check
- Internal-ID
- Counter
-
- Zeitdifferenz der timestamps ("phishing check")
-
vvtlhejdeeribrtcdttjgdtgcvnnglrnfrhjcjchdhdg
|
modhex_decode()
|
ffda638233c71cd02dd852d50fbb5acb4c6808062625
/ \
ffda638233c7 1cd02dd852d50fbb5acb4c6808062625
public id |
aes_decrypt(K)
|
ccff5e92d4e80300b55a2701d3ea0ee9
|
ccff5e92d4e8 0003 275ab5 01 ead3 e90e
internal id s.count timestamp s.use rand crc
HOTP RFC 4226
Algorithmus
- moving factor: 64-bit counter C
- secret: 128-bit HMAC key K
- >= 6 Ziffern
Truncate()
- Verkürzen der MAC auf d Ziffern
- 31-bit Zahl x exrahieren
index = mac[19] & 0xf;
x = mac[index] << 24
| mac[index+1] << 16
| mac[index+2] << 8
| mac[index+3];
x &= 0x7fffffff;
- otp = x mod 10^d
Validation
- ?
- lookahead: akzeptiere
- 6 Ziffern 20 bits. mit lookahead = 8 17 bits
- Serverseitiges throttling um Brute-Force Angriffe zu erschweren
TOTP RFC 6238
- HOTP mit zeitbasiertem Counter
- : Startzeit (unix time)
- : time step
ORCA RFC 6287
- Generalisierung/Erweiterung von HOTP/TOTP
- (mutual) challenge-response
- SHA1 nicht fest verdrahtet
- nicht wirklich verbreitet
- Problem: wie bekommt man die Challenge in das Token?
ORCA CryptoFunction
- OCRA = CryptoFunction(K, DataInput)
- CryptoFunction = HOTP-H-n
- SHA-1, SHA256, SHA512
- n - Anzahl der Ziffern 4-10 oder 0 (= keiner Verkürzung)
- DataInput = OCRASuite | 00 | C | Q | P | S | T
- OCRASuite - mode of operation
- C - Counter (optional)
- Q - Challenge
- P - hashed password/pin (optional)
- S - session information (optional)
- T - timestamp (optional)
ORCA Suites
- OCRASuite = 'Algorithm:CryptoFunction:DataInput'
- "OCRA-1:HOTP-SHA512-8:C-QN08-PSHA1"
- OCRA-1: OCRA Version 1
- HOTP-SHA512-8: HTOP mit SHA512 verkürzt auf 8 Ziffern
- C-QN08-PSHA1:
- C: mit counter
- QN08: numerische Challenge bis zu 8 Ziffern
- PSHA1: SHA1 des Passworts
- "OCRA-1:HOTP-SHA256-6:QA10-T1M"
- OCRA-1: OCRA Version 1
- HOTP-SHA256-6: HTOP mit SHA256 verkürzt auf 6 Ziffern
- QA10-T1M:
- QA10: alphanumerische Challenge bis zu 10 Zeichen.
- T1M: Timestamp Counter (time step = 1 minute)
Challenge Response Protokoll
CLIENT SERVER
(PROVER) VERIFIER)
| |
| Verifier sends challenge to prover |
| Challenge = Q |
|<---------------------------------------|
| |
| Prover Computes Response |
| R = OCRA(K, {[C] | Q | [P | S | T]}) |
| Prover sends Response = R |
|--------------------------------------->|
| |
| Verifier Validates Response |
| If Response is valid, Server sends OK |
| If Response is not, Server sends NOK |
|<---------------------------------------|
| |
http://tools.ietf.org/rfc/rfc6287.txt
Mututal Challenge Response Protokoll
CLIENT SERVER
(PROVER) (VERIFIER)
| |
| 1. Client sends client-challenge |
| QC = Client-challenge |
|------------------------------------------------->|
| |
| 2. Server computes server-response |
| and sends server-challenge |
| RS = OCRA(K, [C] | QC | QS | [S | T]) |
| QS = Server-challenge |
| Response = RS, QS |
|<-------------------------------------------------|
| |
| 3. Client verifies server-response |
| and computes client-response |
| OCRA(K, [C] | QC | QS | [S | T]) != RS -> STOP |
| RC = OCRA(K, [C] | QS | QC | [P | S | T]) |
| Response = RC |
|------------------------------------------------->|
| |
| 4. Server verifies client-response |
| OCRA(K, [C] | QS | QC | [P|S|T]) != RC -> STOP |
| Response = OK |
|<-------------------------------------------------|
| |
http://tools.ietf.org/rfc/rfc6287.txt