Vmware-Tools and time synchronization: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
# Now we can successfully run <pre>/usr/bin/vmware-config-tools.pl</pre> and follow the instructions. |
# Now we can successfully run <pre>/usr/bin/vmware-config-tools.pl</pre> and follow the instructions. |
||
# Run <code> vmware-toolbox </code> and check button [[Image:screen1.gif|Options->Time synchronization ...]]. |
# Run <code> vmware-toolbox </code> and check button [[Image:screen1.gif|Options->Time synchronization ...]]. |
||
# Unfortunatly the guest OS gives timerevents with maximum 1000Hz, what is to slow fror the Linux-SMP-2.6 default kernel. [http://www.vmware.com/support/kb/enduser/std_adp.php?p_faqid=1420 See] Therfore we have to add the kernel boot options: <code>clock=pit noapic nolapic nosmp</code><pre><nowiki> |
# Unfortunatly the guest OS gives timerevents with maximum 1000Hz, what is to slow fror the Linux-SMP-2.6 default kernel. [http://www.vmware.com/support/kb/enduser/std_adp.php?p_faqid=1420 See] Therfore we have to add the kernel boot options: '''<code>clock=pit noapic nolapic nosmp</code>'''<pre><nowiki> |
||
vi /boot/grub/menu.lst |
vi /boot/grub/menu.lst |
||
# Modified by YaST2. Last modification on Tue Feb 21 12:52:40 UTC 2006 |
# Modified by YaST2. Last modification on Tue Feb 21 12:52:40 UTC 2006 |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
###Don't change this comment - YaST2 identifier: Original name: linux### |
###Don't change this comment - YaST2 identifier: Original name: linux### |
||
title SUSE LINUX 9.3 |
title SUSE LINUX 9.3 |
||
kernel (hd0,0)/boot/vmlinuz ...showopts |
kernel (hd0,0)/boot/vmlinuz ...showopts clock=pit noapic nolapic nosmp |
||
initrd (hd0,0)/boot/initrd |
initrd (hd0,0)/boot/initrd |
||
###Don't change this comment - YaST2 identifier: Original name: floppy### |
###Don't change this comment - YaST2 identifier: Original name: floppy### |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
initrd (hd0,0)/boot/initrd |
initrd (hd0,0)/boot/initrd |
||
</nowiki></pre> |
</nowiki></pre> |
||
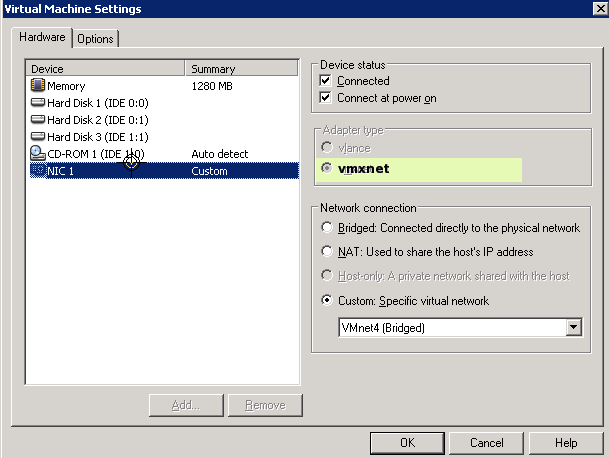
# Shutdown the VM and [[Image:screen2.png|configure the network]] to use <code>vmxnet</code> module instead of <code>pcnet32</code> |
|||
Revision as of 09:08, 2 March 2006
There are several reasons for installing Vmware Tools in the guest-OS:
- Better network performance by using vmxnet module
- May be better Virtual-disk speed because
/etc/init.d/vmware-toolssets uphdparms. - Time synchronization hetween host & guest OS.
Installation:
- Install Virtual Machine (e.g. SuSE 9.3 used here) with
pcnet32network module (default) including the kernel sources. - Run Yast Online Update
you. This updates the packets + kernel + kernel sources. - Reboot.
- Install the Vmware-Tools. We use the
dc:/pub/software/RPM/VMwareTools-5.5.1-19175.i386.rpm
which compiles better with 2.6 kernals then the variant distributed with vmware-gsx-server.rpm -i VMwareTools-5.5.1-19175.i386.rpm
. - Now we have to configure the kernel sources:
cd /usr/srs/linux make cloneconfig make prepare
- Now we can successfully run
/usr/bin/vmware-config-tools.pl
and follow the instructions. - Run
vmware-toolboxand check button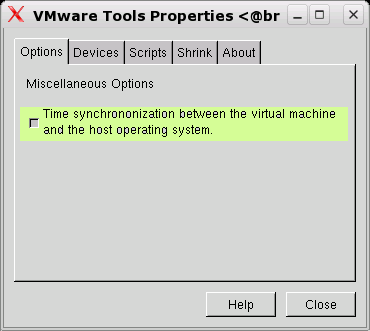 .
. - Unfortunatly the guest OS gives timerevents with maximum 1000Hz, what is to slow fror the Linux-SMP-2.6 default kernel. See Therfore we have to add the kernel boot options:
clock=pit noapic nolapic nosmp
vi /boot/grub/menu.lst # Modified by YaST2. Last modification on Tue Feb 21 12:52:40 UTC 2006 color white/blue black/light-gray default 0 timeout 8 gfxmenu (hd0,0)/boot/message ###Don't change this comment - YaST2 identifier: Original name: linux### title SUSE LINUX 9.3 kernel (hd0,0)/boot/vmlinuz ...showopts clock=pit noapic nolapic nosmp initrd (hd0,0)/boot/initrd ###Don't change this comment - YaST2 identifier: Original name: floppy### title Floppy root (fd0) chainloader +1 ###Don't change this comment - YaST2 identifier: Original name: failsafe### title Failsafe -- SUSE LINUX 9.3 kernel (hd0,0)/boot/vmlinuz ............... 3 initrd (hd0,0)/boot/initrd