Wired Equivalent Privacy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
A WLAN consists of a minimum of two communication partners, also called stations. These stations can communicate with each other using electro-magnetic waves, that have a scope of 20m – 300m. This communication area is known as Basic Service Set (BSS). In order to increase the scope of a wireless network, it is common to introduce access points into the network. These access points relay the traffic from stations and thereby increase the overall communication scope. |
A WLAN consists of a minimum of two communication partners, also called stations. These stations can communicate with each other using electro-magnetic waves, that have a scope of 20m – 300m. This communication area is known as Basic Service Set (BSS). In order to increase the scope of a wireless network, it is common to introduce access points into the network. These access points relay the traffic from stations and thereby increase the overall communication scope. |
||
== |
== Packet Design == |
||
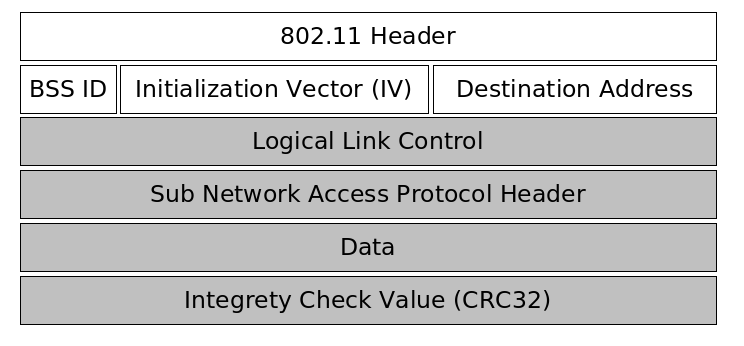
The first part of a packet is unencrypted and contains 802.11 header, the basic service set identifier, an initialization vector chosen by the sender of the packet and the destination hardware address. The second part of the packet is encrypted and carries the data of the above protocols as well as an CRC32 integrety check value. |
The first part of a packet is unencrypted and contains 802.11 header, the basic service set identifier, an initialization vector chosen by the sender of the packet and the destination hardware address. The second part of the packet is encrypted and carries the data of the above protocols as well as an CRC32 integrety check value. |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[Image:packet.png]] |
[[Image:packet.png]] |
||
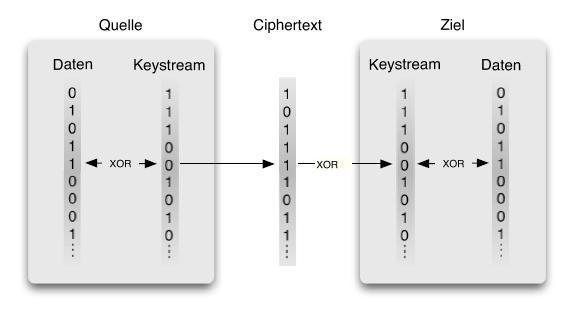
== Encryption & Decryption == |
|||
=== Stream Cipher === |
|||
[[Image:streamcipher.png]] |
|||
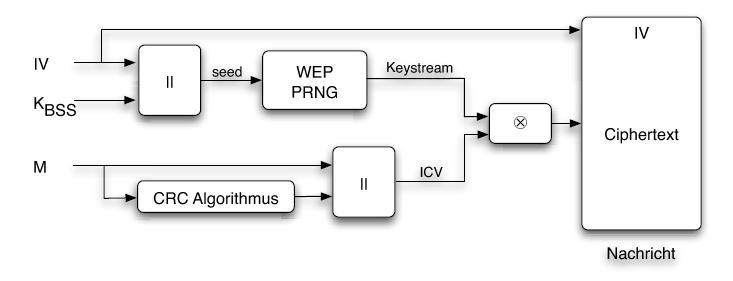
=== Encoding === |
|||
[[Image:encoding.jpg]] |
|||
=== Dencoding === |
|||
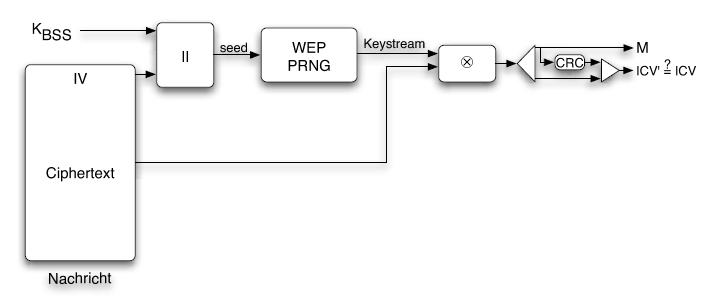
[[Image:decoding.jpg]] |
|||
Revision as of 14:20, 21 June 2007
IEEE 802.11 Standard
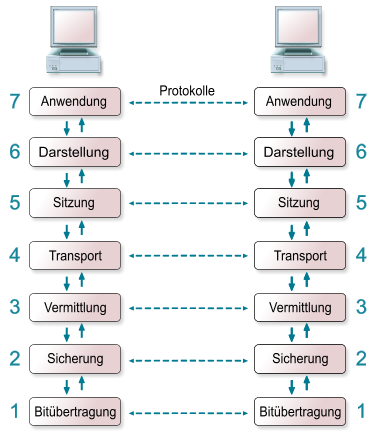
The IEEE 802.11 standard that was published 1997 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The standard specifies the two lowest layers of the OSI (Open System Interconnection) model for local wireless networks. This specification of the two layers (Physical & Media Access Control) is kown as WLAN or WIFI. Common protocols like the TCP/IP or ARP operate on top of these two layers.
Basic Service Set
A WLAN consists of a minimum of two communication partners, also called stations. These stations can communicate with each other using electro-magnetic waves, that have a scope of 20m – 300m. This communication area is known as Basic Service Set (BSS). In order to increase the scope of a wireless network, it is common to introduce access points into the network. These access points relay the traffic from stations and thereby increase the overall communication scope.
Packet Design
The first part of a packet is unencrypted and contains 802.11 header, the basic service set identifier, an initialization vector chosen by the sender of the packet and the destination hardware address. The second part of the packet is encrypted and carries the data of the above protocols as well as an CRC32 integrety check value.
The following picture illustrates the design of WEP packet.